Continuous thinking and working to solve any problem may bring a drastic change throughout the world. Invention of computer is the biggest example of it. In ancient time, people used stones, pebbles, sticks, bones or fingers for counting purposes. In course of time they were always in search of a device which can calculate and can provide them the accurate answer. In this context they have invented amazing and useful products of their time which later on converted into our now a days' PC without which we feel so uncomfortable in our work place.
The development of computer started with mechanical devices. Slowly they were emerged to electro-mechanical devices and finally the electronic computers came into existence.
Let us learn about some devices and computers that are involved in the evolution of computer.
1. Abacus : Around 3000 BC it was developed in China. It is assumed to be the first mechanical device used for calculations. It performs basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. It is made up of wooden frame with rods having beads in each rod. Still it is used to teach calculations to the children, specially multiplication. It can be a substitute for the rote memorisation of table. The people having vision impairment and can't use calculator, can use abacus for calculations. So we can say it is one of the most useful mechanical device from so early age to the present time period.
 |
| Abacus |
It has rectangular strips of rods made up of bones and ivory. Multiplication table embedded in the rods. Using these tables multiplication can be reduced to addition and division to subtractions. |
| Napier's Bone |
3. Pascaline : Invented in 1642 by Blaise Pascal. This mechanical calculator is also known as arithmetic machine. He designed the machine to add and subtract two numbers directly and to perform multiplication and division through repeated addition and subtraction. It used gears, wheels and dials. Numbers were displayed by rotating these wheels. Pascal's Calculator was special for its carry mechanism, where 1 to 9 was added on one dial and when number was changed from 9 to 0 the carry was sent to the next dial.
 |
| Pascaline |
4. Difference Engine : Invented in 1822 by Charles Babbage. It was probably the first automatic mechanical calculator performed mathematical operations automatically. Steam provides the power to make it works.
This mechanical calculator was designed to tabulate polynomial functions. The name difference engine was derived from the method of divided differences, a way to tabulate functions by using a small set of polynomial coefficients, the most common mechanical functions used in engineering, science and navigation are built from logarithmic and trigonometric functions.
 |
| Difference Engine |
5. Analytical Engine : It was designed in 1837 by famous English mathematician and computer pioneer Charles Babbage as the successor of difference engine. It was first general purpose fully program controlled, automatic digital computer. It had the units as arithmetic logic unit, control flow in form of conditional branching and loops, and integrated memory. The structure of the analytical engine was same as the electronic computer design of modern era. It was the most successful achievement of Charles Babbage, that's why he is known as the Father Of Computer. |
| Analytical Engine |
6. Tabulating Machine : It was invented in 1890 by Dr. Herman Hollerith. It was the first electronic machine capable of reading data, processing it and giving output. It has used punch card to give input, record and store information. The machine was developed to help process data for the 1890 US Census. Later models are widely used for business application such as accounting and inventory control.
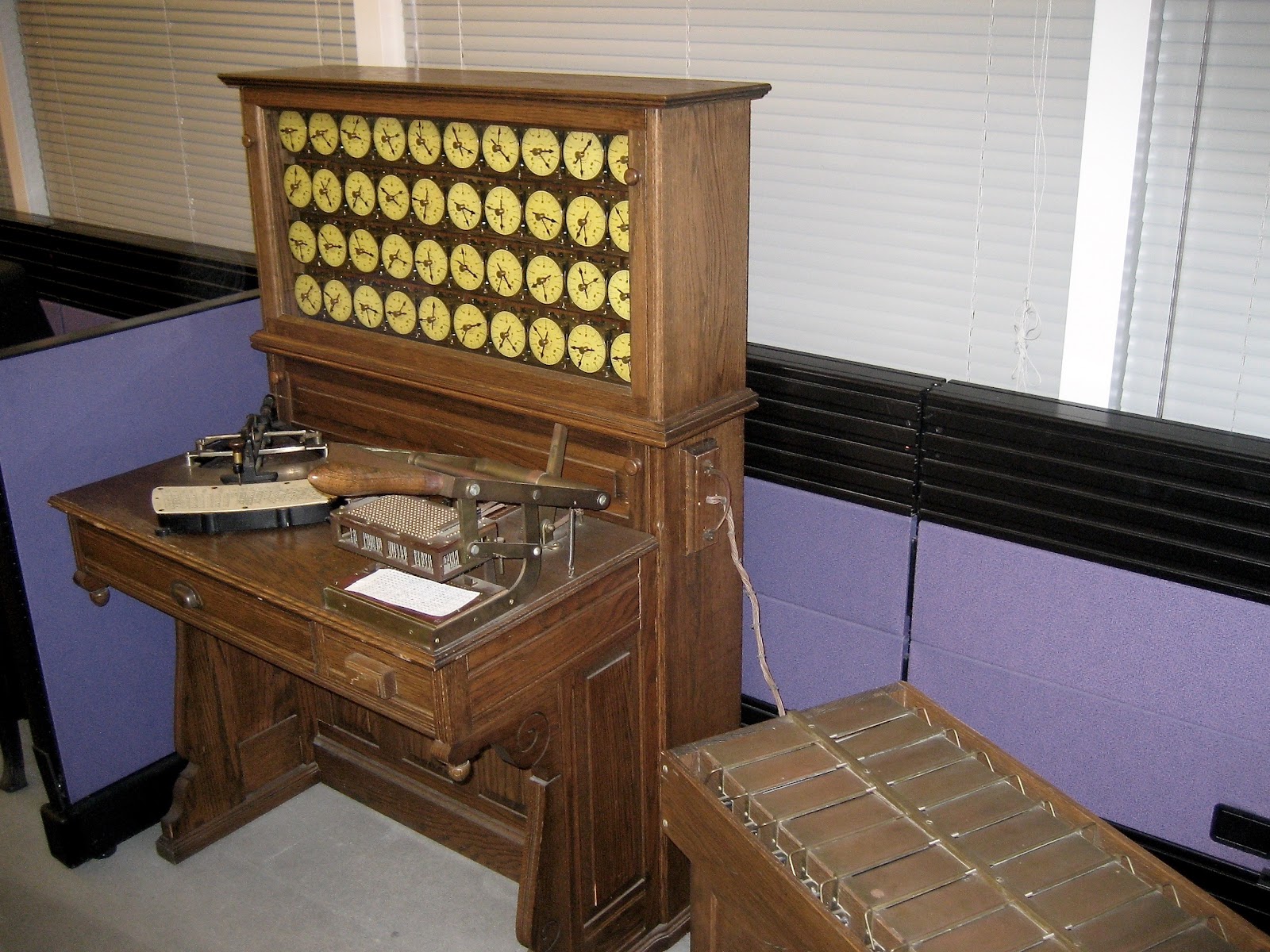 |
| Tabulating Machinde |
7. Mark-I : Invented in 1944 by Howard H. Aiken, was first fully automatic digital computer. It is marked as the beginning of the era of modern computing. It is also known as automatic sequence controlled calculator. It was used in the war effort during the last part of the World War II. One of the first program to run on Mark-I was on 29 March 1944 by John von Neumann. He had to determine whether implosion was a viable choice to detonate the atomic bomb that would be used a year later. Later on it was also used for computing and printing the mathematical tables, which was initial goal of the Charles Babbage for his 'analytical engine' in 1837.
 |
| Mark-I |
8. ENIAC : It stands for Electronic Numeric Integrator And Calculator. It was completed in 1946 by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert, Physics Professors of Ursinus College of the University of Pennsylvania, US. It was first general purpose electronic digital computer and around 1000 times faster than Mark-IENIAC was a large modular computer composed of individual panels to perform different functions. Twenty of these modules were accumulated to perform not only addition and subtraction but can hold a 10 digit decimal number in its memory. Numbers were passed between these units by several general purposes buses. In order to achieve its high speed the panels had to send or receive number. computer was able to save the answer and trigger the next operation. all were done without any moving parts. Key to its versatility was ability to branch, it could trigger different operations, depending on the sign of the computed result.
 |
| ENIAC |
9. EDSAC : Stands for Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator, designed by Maurice Wilkes in 1949. It was first electronic computer that used stored programs. it was faster than ENIAC, ran its first program in 1949, when it calculated a table of square numbers and a list of prime numbers.
 |
| EDSAC |
10. UNIVAC-I : Universal Automatic Computer designed by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert the inventors of the ENIAC in 1951. It was first commercially available electronic computer. It was the first computer to handle both number as well as text data. Its fifth edition was used by CBS to predicts the result of the 1952 presidential election. |
| UNIVAC-I |















No comments:
Post a Comment